Zhang, X., Yuan, J., Zhao, Y., & Qin, B. (2021). Knowledge Enhanced Target-Aware Stance Detection on Tweets. 收入 B. Qin, Z. Jin, H. Wang, J. Pan, Y. Liu, & B. An, Knowledge Graph and Semantic Computing: Knowledge Graph Empowers New Infrastructure Construction (页 171–184). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-6471-7_13
“We argue that the nonalignment between targets and potentially opinioned terms in texts causes such failure and this could be remedied with external knowledge as a bridge.” (Zhang et al., 2021, p. 171) 我们认为,目标与文本中可能有意见的术语之间的不一致导致了这种失败,这可以通过外部知识作为桥梁来补救。
“To this end, we propose RelNet, which leverages multiple external knowledge bases as bridges to explicitly link potentially opinioned terms in texts to targets of interest.” (Zhang et al., 2021, p. 171) 为此,我们提出了 RelNet,它利用多个外部知识库作为桥梁,将文本中可能有意见的术语明确链接到感兴趣的目标。
“Stance detection is the task of classifying attitude of a text towards a given target entity or claim [12]. Its techniques can be utilized for various downstream applications, such as online debates analysis [14,17,20], opinion groups identification [1,15], election results prediction [10], and fake news detection [7].” (Zhang et al., 2021, p. 171) 姿态检测是对文本对给定目标实体或声明的态度进行分类的任务 [12]。其技术可用于各种下游应用,例如在线辩论分析 [14,17,20]、意见群体识别 [1,15]、选举结果预测 [10] 和假新闻检测 [7]。
“However, all these methods learn the relation between opinioned terms and targets implicitly. And text features alone usually fail to provide adequate context to capture such relations.” (Zhang et al., 2021, p. 172) 然而,所有这些方法都隐式地学习了有意见的术语和目标之间的关系。单独的文本特征通常无法提供足够的上下文来捕捉这种关系。
“CKEMN [5] exploits ConceptNet to expand the concept words for entities in the text and further models the relation between targets and those concepts with attention.” (Zhang et al., 2021, p. 172) CKEMN [5] 利用 ConceptNet 扩展文本中实体的概念词,并进一步建模目标与那些具有注意力的概念之间的关系。
“AEKFW [8] obtain relevant concept words for targets and learns relation representations between those concepts and each word in the text.” (Zhang et al., 2021, p. 172) AEKFW [8] 获取目标的相关概念词,并学习这些概念与文本中每个词之间的关系表示。
“RelNet begins with expanding targets with knowledge from multiple sources. Then it chooses opinioned terms in the text by measuring the similarity to expanded entities from knowledge.” (Zhang et al., 2021, p. 172) RelNet 从使用来自多个来源的知识扩展目标开始。然后它通过测量与知识中扩展实体的相似性来选择文本中有观点的术语。
“We propose a novel method named RelNet, which explicitly connects targets and potential opinioned terms in the text.” (Zhang et al., 2021, p. 173) 我们提出了一种名为 RelNet 的新方法,它明确地将文本中的目标和潜在的自以为是的术语联系起来。
“We provide a simple way to fuse knowledge from multiple external knowledge bases and outperform the BERT model by a large margin, especially on cases where targets are not explicitly mentioned in texts.” (Zhang et al., 2021, p. 173) 我们提供了一种简单的方法来融合来自多个外部知识库的知识,并大大优于 BERT 模型,尤其是在目标未在文本中明确提及的情况下。
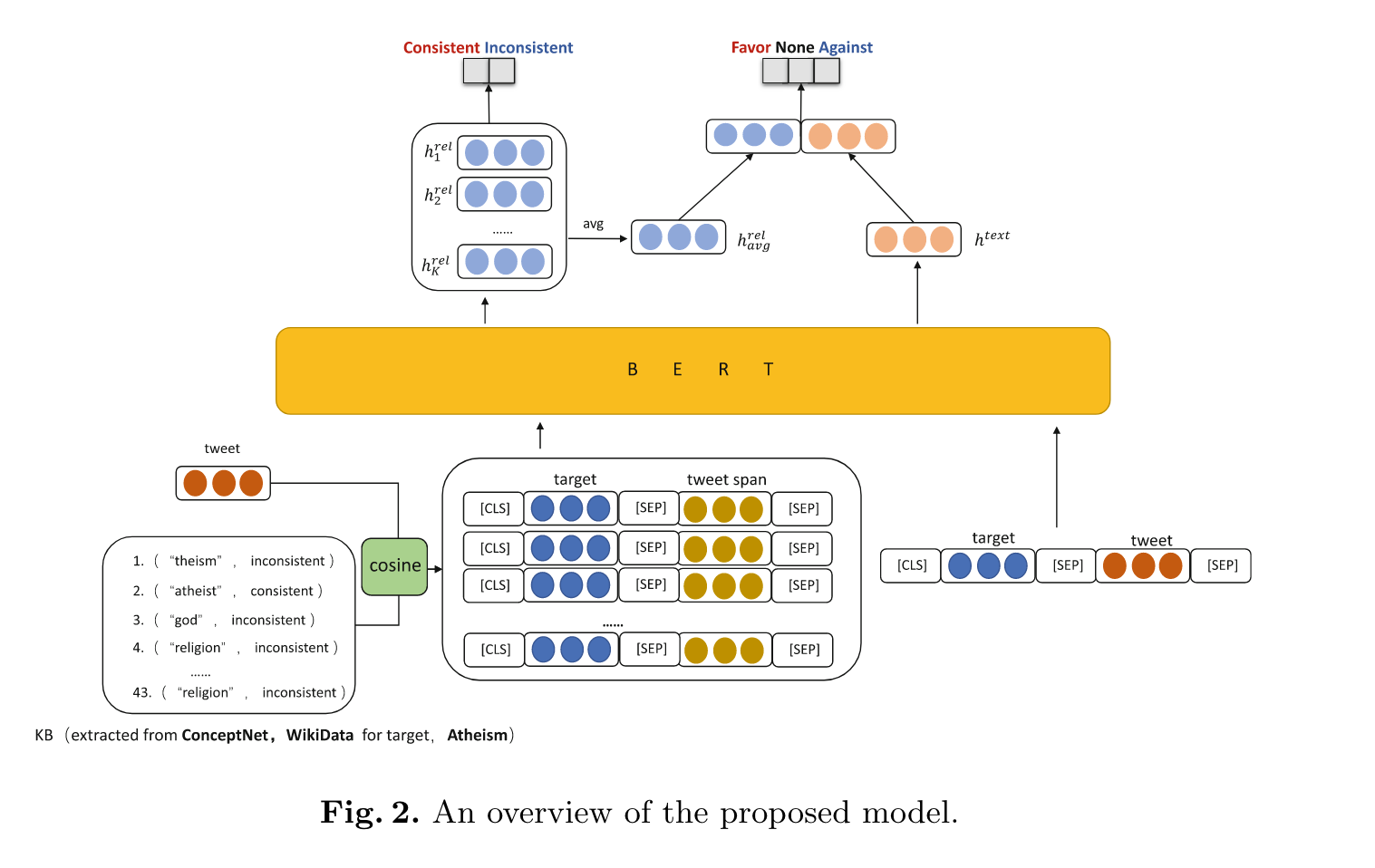
“The overall architecture of our model is shown in Fig. 2. It consists of four main components: 1) Target Related Knowledge Filtration Module, acquiring knowledge triples from multiple knowledge bases, filtering knowledge, and integrating knowledge relations into two categories: consistent and inconsistent; 2) Textual Encoding Module, getting target-aware textual representation htext of target and tweet; 3) Opinioned Terms Encoder Module, selecting K opinioned terms in tweets using target related knowledge, and getting the opinioned terms feature referring to target hrel i ,i ∈{1, 2,…,K}; 4) Classification Module, for introducing the relation between target and opinioned terms, we use a multi-task framework to combine the relation classification task and the stance detection task.” (Zhang et al., 2021, p. 174) 我们模型的总体架构如图2所示。它由四个主要部分组成:1)目标相关知识过滤模块,从多个知识库中获取知识三元组,过滤知识,并将知识关系整合为两类:一致和不一致; 2) Textual Encoding Module,获取target和tweet的target-aware文本表示htext; 3) Opinioned Terms Encoder Module,利用目标相关知识在推文中选取K个opinioned terms,得到指向目标hrel i ,i ∈{1, 2,…,K}的opinioned terms特征; 4)分类模块,为了引入目标词和意见词之间的关系,我们使用多任务框架将关系分类任务和姿态检测任务结合起来。
“The goal of the target related knowledge filtration module is to get the target related knowledge triples from the external knowledge base, and organize the relation of knowledge into a suitable format (consistent, inconsistent) for stance detection. This module is composed of three parts: knowledge acquisition, knowledge filtering, and relation integration.” (Zhang et al., 2021, p. 175) 目标相关知识过滤模块的目标是从外部知识库中获取目标相关知识三元组,并将知识关系组织成适合姿态检测的格式(一致,不一致)。该模块由知识获取、知识过滤和关系整合三部分组成。
“Knowledge Acquisition. Specifically, we take two structured knowledge bases, ConceptNet and WikiData. ConceptNet mainly contains commonsense knowledge, WikiData mainly contains social knowledge.” (Zhang et al., 2021, p. 175) 知识获取。具体来说,我们采用两个结构化知识库,ConceptNet 和 WikiData。 ConceptNet主要包含常识性知识,WikiData主要包含社会知识。
“In this way, we build a knowledge base KB D of triples (tkb,r,c) ∈ D for this dataset , each consisting of a target tkb, a relation r, and a knowledge concept in the WikiData or ConceptNet c, e.g. (atheism,different from,religion).” (Zhang et al., 2021, p. 175) 通过这种方式,我们为该数据集构建了一个三元组 (tkb,r,c) ∈ D 的知识库 KB D,每个知识库由一个目标 tkb、一个关系 r 和 WikiData 或 ConceptNet c 中的一个知识概念组成,例如(无神论,不同于宗教)。
“Delete triples whose knowledge words do not appear in all selected pairs (knowledge word, tweet spans). Through the above process, we filter out irrelevant knowledge in the knowledge base D” (Zhang et al., 2021, p. 176) 删除其知识词未出现在所有选定对(知识词、推文跨度)中的三元组。通过以上过程,我们过滤掉了知识库D中不相关的知识
“Meanwhile, previous work [8] has shown that extracting consistent and inconsistent relations from commonsense knowledge is a promising approach to enhancing stance detection performance, therefore we unified the relations in ConceptNet and WikiData, and integrated the originally complicated relation into a consistent (1) and inconsistent (−1), e.g.from (atheism,differentfrom,religion)to(atheism, −1, religion).” (Zhang et al., 2021, p. 176) 同时,之前的工作[8]表明,从常识知识中提取一致和不一致的关系是提高姿态检测性能的一种很有前途的方法,因此我们统一了 ConceptNet 和 WikiData 中的关系,并将原本复杂的关系整合为一致的(1)和不一致的 (−1),例如从 (atheism,differentfrom,religion) 到 (atheism, −1, religion)。
“The content in the tweet is obtained by sliding a window of size w across the sentence, producing a sequence of word fragments of length w , w = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, as the tweet-spans of the tweet.” (Zhang et al., 2021, p. 176) 推文中的内容是通过在句子上滑动大小为 w 的窗口获得的,产生长度为 w 的单词片段序列,w = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5},作为推文的 tweet-spans .
“For a pair of the target t and tweet s , we take knowledge-word c in (tkb,r,c) ∈ D which tkb is the same as target t and take tweet-spans from the tweet.” (Zhang et al., 2021, p. 176) 对于一对目标 t 和推文 s ,我们在 (tkb,r,c) ∈ D 中获取知识词 c,其中 tkb 与目标 t 相同,并从推文中获取推文跨度。
“The opinioned terms representation hrel avg of a tweet is obtained by averaging {hrel 1 ,hrel 2 …hrel K }” (Zhang et al., 2021, p. 177) 推文的观点术语表示 hrel avg 是通过平均 {hrel 1 ,hrel 2 …hrel K } 获得的
“To jointly leverage the tweet text, target, and relation information between opinioned terms in the tweet and the target, the opinioned terms presentations and the target-aware textual representation are concatenated and fed into the stance classifier.” (Zhang et al., 2021, p. 177) 为了共同利用推文文本、目标以及推文中的观点词与目标之间的关系信息,观点词表示和目标感知文本表示被连接起来并输入到立场分类器中。
“MITRE [25]: The best system in SemEval-2016 subtaskA is MITRE. This model uses two RNNs: the first one is trained to predict the task-relevant hashtags on a very large unlabeled Twitter corpus. This network is used to initialize the second RNN classifier, which was trained with the provided subtask-A data.” (Zhang et al., 2021, p. 178) MITRE [25]:SemEval-2016 子任务 A 中最好的系统是 MITRE。该模型使用两个 RNN:第一个被训练来预测一个非常大的未标记 Twitter 语料库中与任务相关的主题标签。该网络用于初始化第二个 RNN 分类器,该分类器使用提供的子任务 A 数据进行训练。
“However, CKEMN did not integrate different relationships according to the requirements of stance detection task. Our model integrates the relationship into consistent and inconsistent, and establishes the relationship between target and opinioned terms in tweets.” (Zhang et al., 2021, p. 179) 然而,CKEMN 并没有根据姿态检测任务的要求整合不同的关系。我们的模型将关系整合为一致和不一致,并在推文中建立目标词和观点词之间的关系。
“This proves that our model can effectively establish a relation between targets and opinioned terms for texts where targets are not mentioned, thus help to improve the performance of stance detection.” (Zhang et al., 2021, p. 180) 这证明我们的模型可以有效地建立目标和未提及目标的文本之间的关系,从而有助于提高姿态检测的性能。
“It can be seen from Table 8 that after adding anti-knowledge into D, the performance of the model declines, which is contrary to our expectations. It is possible that manually selected anti words are not suitable for the dataset, resulting in a lot of noise.” (Zhang et al., 2021, p. 181) 从表8可以看出,在D中加入反知识后,模型的性能有所下降,这与我们的预期相反。有可能是人工选择的反词不适合数据集,导致噪声很大。